Fluorouracil 250mg/5ml Injection
Fluorouracil
250mg/5ml Injection
Fluorouracil Injection, USP is available in two pharmacy bulk vials as follows: Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.] Protect from light. Retain in carton until time of use. Note: Although fluorouracil solution may discolor slightly during storage, the potency and safety are not adversely affected. Also available as follows: 10 mL vials are packaged 10 vials per shelf pack. Procedures for proper handling and disposal of anticancer drugs should be considered. Several guidelines on this subject have been published.1 to 7 There is no general agreement that all of the procedures recommended in the guidelines are necessary or appropiate.
PHARMACY BULK PACKAGES:
Fluorouracil Injection, USP 50 mg/mL,Volume:2.5 g/50 mL vial
Fluorouracil Injection, USP 50 mg/mL, Volume:5 g/100 mL vial
SINGLE DOSE VIALS:
Fluorouracil Injection, USP 50 mg/mL, Volume:500 mg/10 mL vial
Fluorouracil Injection, USP 50 mg/mL, Volume:1 g/20 mL vial
20 mL vials are packaged 10 vials per shelf pack.
Note: Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.If a precipitate occurs due to exposure to low temperatures, resolubilize by heating to 140°F and shaking vigorously; allow to cool to body temperature before using.
Fluorouracil
250mg/5ml Injection
What Fluorouracil Injection is and what it is used for
The name of medicine is ‘Fluorouracil 50 mg/ml, Solution for Injection or Infusion’ but in the rest of the leaflet it will be called ‘Fluorouracil Injection’.
What Fluorouracil Injection is
Fluorouracil Injection contains the active ingredient Fluorouracil. It is an anti-cancer medication.
What Fluorouracil Injection is used for
Fluorouracil Injection is used to treat many common cancers, particularly cancers of the large bowel, oesophagus, pancreas, stomach, head and neck and breast. It may be used in combination with other anti-cancer medicines and radiotherapy.
What you need to know before you use Fluorouracil Injection
Do not use Fluorouracil Injection
- if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to Fluorouracil or any of the other ingredients of Fluorouracil Injection
- if you have serious infections (e.g. Herpes zoster, chickenpox)
- if your tumour is non-malignant.
- if you have been very much weakened by long illness.
- if your bone marrow has been damaged by other treatments(including radiotherapy).
- if you are taking brivudin, sorivudin and analogues (an antiviral drug)
- if you are pregnant or breast feeding women
- if you have serious impaired liver function
- if you are homozygotic for dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) enzyme
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist or nurse before using Fluorouracil Injection. Take special care with Fluorouracil Injection:
- if the number of cells in your blood become too low (you will have blood tests to check this)
- if you have oral ulceration, fever or hemorrhage at any site or weakness (these symptoms may be the consequence of
the very low number of cells in your blood),
- if you have any problems with your kidneys
- if you have any problems with your liver including jaundice (yellowing of the skin)
- if you problem with your heart. Tell your doctor if you experience any chest pain during treatment.
- if you have reduced activity/deficiency of the enzyme DPD (dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase).
- If you have had high-dose pelvic radiation.
- if you have gastrointestinal side effects (stomatitis, diarrhoea, bleeding from the G.I. tract) or hemorrhage at any site.
Other medicines and Fluorouracil Injection
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines.
- Methotrexate (an anti-cancer medicine)
- Metronidazole (an antibiotic)
- Calcium leucovorin (also called calcium folinate - used to reduce the harmful effects of anti-cancer medicines)
- Allopurinol (used to treat gout)
- Cimetidine (used to treat stomach ulcers)
- Warfarin (used to treat blood clots)
- Interferon alpha 2a; brivudin, sorivudin and analogues (an antiviral)
- Cisplatin (an anticancer medicine)
- Phenytoin (used to control epilepsy/fits and irregular heart rhythm)
- Vaccines
- Vinorelbine (an anti-cancer medicine)
- Cyclophosphamide (an anti-cancer medicine)
- Levamisol (medicine used to treat worm infection)
- Tamoxifen (an anti-cancer medicine)
The above medicines affect the effect of Fluorouracil.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility
You must not take this drug if you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. If you are a women of childbearing potential you must use an effective method of contraception while taking this drug and atleast for 6 months afterwards. If pregnancy occurs during your treatment you must inform your doctor and should use genetic counsellation.
Since it is not known whether fluorouracil passes into breast milk, breast-feeding must be discontinued if the mother is treated with Fluorouracil Injection.
If you are a man you should avoid father a child during and for up to 6 months following cessation of treatment with Flurouracil Injection. You are advice to sought conservation of sperm prior to treatment because of the possibility of irreversible infertility due to therapy with Flurouracil Injection.
Ask your doctor for advice before taking any medicine.
Driving and using machines
Do not drive or use machines because fluorouracil may produce side effects like nausea and vomiting. It can also produce adverse event on your nervous system and visual changes. If you experience any of this effect, do not drive or use any tools or machines, it may impair your ability to drive or use machines.
How to use Fluorouracil Injection
The dose of medicine given to you will depend on your medical condition, your body weight, if you have had recent surgery and how well your liver and kidneys are working. It will also depend on the results of your blood tests. Your first course of treatment may be given daily or at weekly intervals. Further courses may be given according to your response to treatment. You may also receive treatment in combination with radiotherapy.
The medicine may be diluted with glucose solution, sodium chloride solution or Water for injections before it is given to you. It will be given into a vein either as a normal injection or a slow injection via a drip (infusion).
If you are given more Fluorouracil Injection than you should
As this medicine will be given to you whilst you are in hospital is unlikely that you will be given too little or too much, however, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you have any concerns.
You will need to have blood tests during and after treatment with Fluorouracil Injection to check the levels of cells in your blood. Treatment may have to be stopped if the level of white blood cells drops too low.
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, severe mucositis and gastrointestinal ulceration and bleeding may occur if you have too much fluorouracil. If you have any further question on the use of this product ask your doctor.
Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If any of the following happen, tell your doctor immediately:
- severe allergic reaction – you may experience a sudden itchy rash (hives), swelling of the hands, feet, ankles, face, lips, mouth or throat (which may cause difficulty in swallowing or breathing), and you may feel you are going to faint.
- chest pains
- your bowel motions are bloodstained or black
- your mouth becomes sore or develops ulcers
- numbness, tingling or tremor in the hands or feet
- quickening of your heart rate and breathlessness
- feeling confused or feeling unsteady on your feet, coordination problems in arms and legs, thinking/speech difficulties, vision/memory problems
Very common side effects (more than 1 in 10 patients):
- Ischemic ECG abnormalities(an insufficient supply of blood to an organ, usually due to a blocked artery)
- Neutropenia (an abnormally low level of neutrophils in the blood)
- Leucopenia (an abnormally low number of white blood cells in the circulating blood)
- Anemia (condition in which the circulating red cell mass is insufficient)
- Decrease in the production of blood cells
- High fever and a sharp drop in circulating granular white blood
- Inflammation of the rectum or anus The inflammation of the lining of the mouth and
- Loss of appetite
- Pharyngitis (inflammation of the mucous membranes lining the
- Watery diarrhoea
- Nausea
- Delayed wound healing
- Bleeding from the nose
- Hair loss
- Hand-foot syndrome is a toxic skin
- General weakness
- Inflammation of the mucous
- lining of any of the structures in the mouth
- Increase in uric acid in the blood
- Inflammation of the esophagus
- Tiredness
Common side effects (less than 1 in 10 patients):
Angina pectoris (Severe pain in the chest associated with an insufficient supply of blood to the heart)
Uncommon side effects (less than 1 in 100 patients):
- Abnormality in the heart'srhythm
- Myocarditis (inflammatory disease of the heart muscle)
- Symptoms of Parkinson's disease (a progressive movement disorder marked by tremors, rigidity, slow movements)
- Rhythmic motions of the eyes
- Dehydration
- Cardiac shock
- Heart attack
- Heart insufficiency
- Bacterial infection in the bloodstream or body tissues
- Heart insufficiency
- Pyramidal signs
- Myocardial ischemia (a loss of oxygen to the heart muscle)
- Dilative cardiomyopathy (a type of heart disease in which the heart muscle is abnormally enlarged,
thickened and/or stiffened)
- Sleepiness
- Gastrointestinal ulceration and bleeding, casting off the skin
- Feeling of being sick
- Inflammation of the skin
- Skin alterations e.g. dry skin, fissure erosion, Redness of the skin, pruritic maculopapular rash (rash that had originated on the lower extremities and had progressed to the arms, and then to the chest)
- A skin eruption accompanying certain infectious diseases
- A layer or mass of dead tissue separated from surrounding living tissue, as in a wound, a sore, or an inflammation.
Rare side effects (more than 1 in 10,000 but less than 1 in 1,000 patients):
- Insufficient blood flow in brain, intestine and peripheral organs
- discoloration of the fingers, toes, and occasionally other areas
- Generalized allergic reaction
- swelling (inflammation) of a vein caused by a blood clot
- severe, whole-body allergic reaction (anaphylaxis)
- Development of a clot within blood vessels, can occur in arteries or veins
- systemic vasodilation (widening of blood vessels) which results in low blood pressure
- confusion
- Increase of T4 (total thyroxin), increase of T3 (total trijodthyronin
Very rare side effects (less than 1 in 10,000 patients):
- Cardiac arrest (sudden cessation of heartbeat and cardiac function)
- Sudden cardiac death (unexpected death due to heart problems)
- Symptoms of leucoencephalopathy (diseases affecting the white substance of the brain) including
- ataxia (loss of the ability to coordinate muscular movement)
- Acute cerebellar syndrome
- Difficulty in articulating words
- Confusion
- Mental confusion or impaired awareness especially regarding to time, place or identity
- Partial or total loss of the ability to communicate verbally or using written words.
- Abnormal muscular weakness or fatigue
- Convulsion or coma in patients receiving high doses of 5-fluorouracil and in patients with Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency
- kidney failure
- Damage of liver cells (cases with fatal outcome
Not Known (Frequency can not be estimated):
- fever
- numbness or weakness of the arms and legs
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.B y reporting side effects you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
These are serious side effects. You may need urgent medical attention.
How to store Fluorouracil Injection
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date, which is stated on the Label and carton after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Store below 25°C. Do not refrigerate or freeze.
Keep container in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
Single use only. Discard any unused portion.
Shelf Life after dilution
Chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 24 hours at 25°C with Glucose 5% or Sodium Chloride 0.9% Injection B.P or Water for Injections B.P at concentration 0.98 mg/ml of Fluorouracil. However from a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately. If not used immediately, in-use storage times and conditions prior to use are the responsibility of the user and would normally not be longer than 24 hours at 2-8°C, unless dilution has taken place in controlled and validated aseptic conditions.
Do not use if the product appears brown or dark yellow in solution.
Do not use if you notice that the container is damaged or particles/crystals are visible.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines no longer used. These measures will help to protect the environment.
Contents of the pack and other information
What Fluorouracil Injection contains
- The active substance in Fluorouracil Injection is fluorouracil.
- The other ingredients are water for injections, sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid.
What Fluorouracil Injection looks like and content of the pack
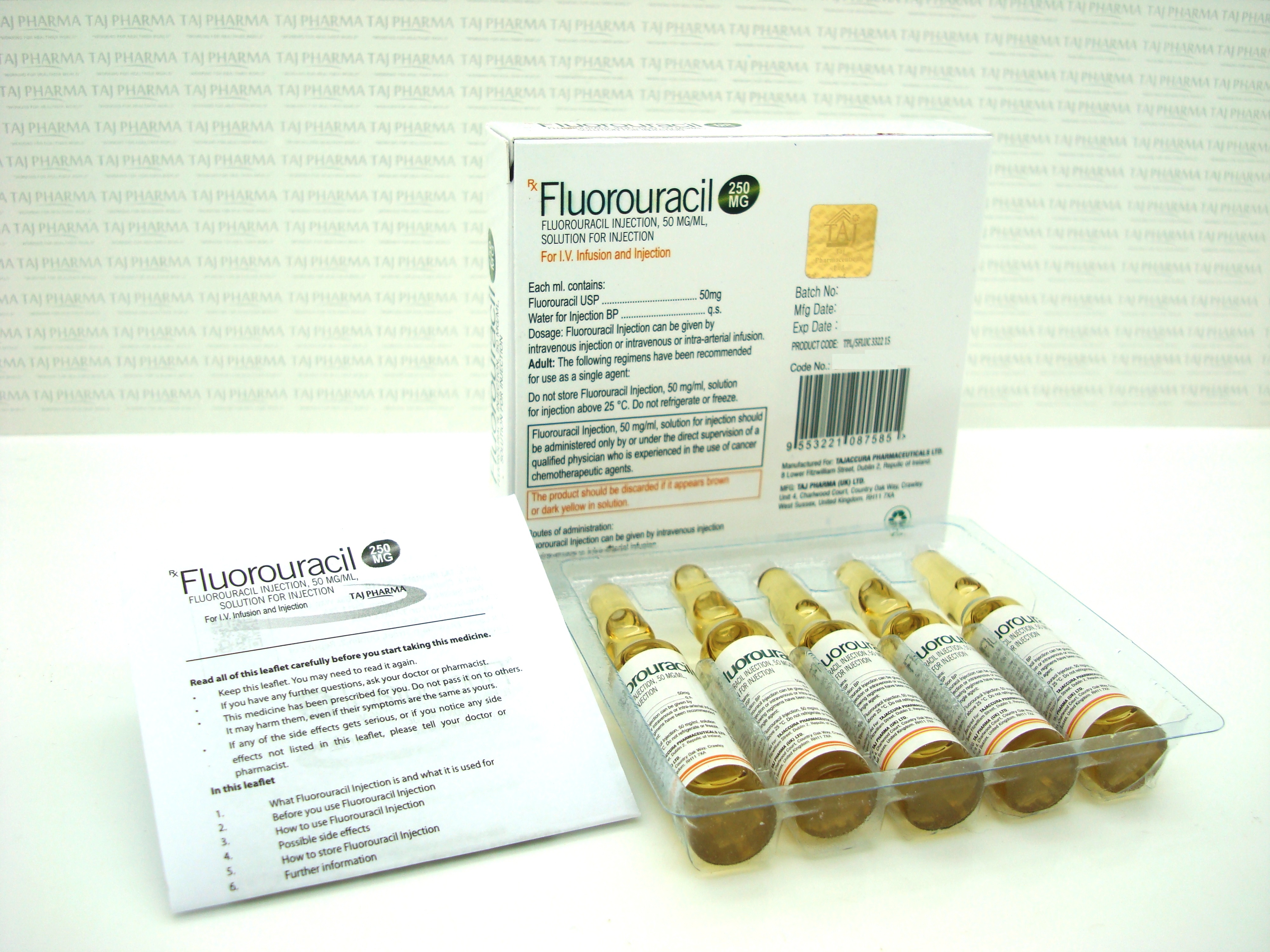
1ml of solution contains 50 mg of fluorouracil (as sodium salt ).
Fluorouracil solution for Injection or Infusion is a clear, almost colourless solution in a Type I clear glass vial with rubber closure.
- Each 5 ml vial contains 250 mg of fluorouracil
- Each 10 ml vial contains 500 mg of fluorouracil
- Each 20 ml vial contains 1000 mg of fluorouracil
- Each 50 ml vial contains 2500 mg of fluorouracil
- Each 100 ml vial contains 5000 mg of fluorouracil
Not all pack sizes may be marketed
Fluorouracil
250mg/5ml Injection
DESCRIPTION
Fluorouracil Injection, USP an antineoplastic antimetabolite, is a colorless to faint yellow aqueous, sterile, nonpyrogenic injectable solution available in a 50 mL and 100 mL Pharmacy Bulk Package for intravenous administration. Each mL contains 50 mg fluorouracil in water for injection USP, pH is adjusted to approximately 8.6 to 9.4 with sodium hydroxide.
Chemically, fluorouracil, a fluorinated pyrimidine, is 5-fluoro-2,4 (1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione. It is a white to practically white crystalline powder which is sparingly soluble in water. The molecular weight of fluorouracil is 130.08 and the structural formula is:

Molecular formula: C4H3FN2O2 Molecular weight:130.08
A Pharmacy Bulk Package is a container of a sterile preparation for parenteral use that contains many single doses. The contents are intended for use in a pharmacy admixture program and are restricted to the preparation of admixtures for intravenous infusion.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
There is evidence that the metabolism of fluorouracil in the anabolic pathway blocks the methylation reaction of deoxyuridylic acid to thymidylic acid. In this manner, fluorouracil interferes with the synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and to a lesser extent inhibits the formation of ribonucleic acid (RNA). Since DNA and RNA are essential for cell division and growth, the effect of fluorouracil may be to create a thymine deficiency which provokes unbalanced growth and death of the cell. The effects of DNA and RNA deprivation are most marked on those cells which grow more rapidly and which take up fluorouracil at a more rapid rate.
Following intravenous injection, fluorouracil distributes into tumors, intestinal mucosa, bone marrow, liver and other tissues throughout the body. In spite of its limited lipid solubility, fluorouracil diffuses readily across the blood-brain barrier and distributes into cerebrospinal fluid and brain tissue.
Seven to twenty percent of the parent drug is excreted unchanged in the urine in six hours; of this over 90% is excreted in the first hour. The remaining percentage of the administered dose is metabolized, primarily in the liver. The catabolic metabolism of fluorouracil results in degradation products (e.g.,CO2, urea and α-fluoro-β-alanine) which are inactive. The inactive metabolites are excreted in the urine over the next 3 to 4 hours. When fluorouracil is labeled in the six carbon position, thus preventing the 14C metabolism to CO2, approximately 90% of the total radioactivity is excreted in the urine. When fluorouracil is labeled in the two carbon position approximately 90% of the total radioactivity is excreted in expired CO2. Ninety percent of the dose is accounted for during the first 24 hours following intravenous administration.
Following intravenous administration of fluorouracil, the mean half-life of elimination from plasma is approximately 16 minutes, with a range of 8 to 20 minutes, and is dose dependent. No intact drug can be detected in the plasma 3 hours after an intravenous injection.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Fluorouracil Injection, USP is effective in the palliative management of carcinoma of the colon, rectum, breast, stomach and pancreas.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Fluorouracil Injection, USP therapy is contraindicated for patients in a poor nutritional state, those with depressed bone marrow function, those with potentially serious infections or those with a known hypersensitivity to Fluorouracil Injection, USP.
WARNINGS
It is recommended that Fluorouracil Injection, USP be given only by or under the supervision of a qualified physician who is experienced in cancer chemotherapy and who is well versed in the use of potent antimetabolites. Because of the possibility of severe toxic reactions, it is recommended that patients be hospitalized at least during the initial course of therapy.
These instructions should be thoroughly reviewed before administration of Fluorouracil Injection, USP.
THE DAILY DOSE OF FLUOROURACIL INJECTION, USP IS NOT TO EXCEED 800 MG. IT IS RECOMMENDED THAT PATIENTS BE HOSPITALIZED DURING THEIR FIRST COURSE OF TREATMENT.
Fluorouracil Injection, USP should be used with extreme caution in poor risk patients with a history of high-dose pelvic irradiation or previous use of alkylating agents, those who have a widespread involvement of bone marrow by metastatic tumors or those with impaired hepatic or renal function.
Rarely, unexpected, severe toxicity (e.g., stomatitis, diarrhea, neutropenia and neurotoxicity) associated with 5-fluorouracil has been attributed to deficiency of dipyrimidine dehydrogenase activity. A few patients have been rechallenged with 5-fluorouracil and despite 5-fluorouracil dose lowering, toxicity recurred and progressed with worse morbidity. Absence of this catabolic enzyme appears to result in prolonged clearance of 5-fluorouracil.
Pregnancy: Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category D.
Fluorouracil may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Fluorouracil has been shown to be teratogenic in laboratory animals. Fluorouracil exhibited maximum teratogenicity when given to mice as single intraperitoneal injections of 10 to 40 mg/kg on day 10 or 12 of gestation. Similarly, intraperitoneal doses of 12 to 37 mg/kg given to rats between days 9 and 12 of gestation and intramuscular doses of 3 to 9 mg given to hamsters between days 8 and 11 of gestation were teratogenic. Malformations included cleft palates, skeletal defects and deformed appendages, paws and tails. The dosages which were teratogenic in animals are 1 to 3 times the maximum recommended human therapeutic dose. In monkeys, divided doses of 40 mg/kg given between days 20 and 24 of gestation were not teratogenic.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies with fluorouracil in pregnant women. While there is no evidence of teratogenicity in humans due to fluorouracil, it should be kept in mind that other drugs which inhibit DNA synthesis (e.g., methotrexate and aminopterin) have been reported to be teratogenic in humans. Women of childbearing potential should be advised to avoid becoming pregnant. If the drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking the drug, the patient should be told of the potential hazard to the fetus. Fluorouracil should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Combination Therapy
Any form of therapy which adds to the stress of the patient, interferes with nutrition or depresses bone marrow function will increase the toxicity of fluorouracil.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Fluorouracil is a highly toxic drug with a narrow margin of safety. Therefore, patients should be carefully supervised, since therapeutic response is unlikely to occur without some evidence of toxicity. Severe hematological toxicity, gastrointestinal hemorrhage and even death may result from the use of fluorouracil despite meticulous selection of patients and careful adjustment of dosage. Although severe toxicity is more likely in poor risk patients, fatalities may be encountered occasionally even in patients in relatively good condition.
Therapy is to be discontinued promptly whenever one of the following signs of toxicity appears:
- Stomatitis or esophagopharyngitis, at the first visible sign.
- Leukopenia (WBC under 3500) or a rapidly falling white blood count.
- Vomiting, intractable.
- Diarrhea, frequent bowel movements or watery stools.
- Gastrointestinal ulceration and bleeding.
- Thrombocytopenia (platelets under 100,000).
- Hemorrhage from any site.
The administration of 5-fluorouracil has been associated with the occurrence of palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, also known as hand-foot syndrome. This syndrome has been characterized as a tingling sensation of hands and feet which may progress over the next few days to pain when holding objects or walking. The palms and soles became symmetrically swollen and erythematous with tenderness of the distal phalanges, possibly accompanied by desquamation. Interruption of therapy is followed by gradual resolution over 5 to 7 days. Although pyridoxine has been reported to ameliorate the palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, its safety and effectiveness has not been established.
Information for Patients
Patients should be informed of expected toxic effects, particularly oral manifestations. Patients should be alerted to the possibility of alopecia as a result of therapy and should be informed that it is usually a transient effect.
Laboratory Tests
White blood counts with differential are recommended before each dose.
Drug Interactions
Leucovorin calcium may enhance the toxicity of fluorouracil.
Also see WARNINGS section.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility:
Carcinogenesis
Long-term studies in animals to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of fluorouracil have not been conducted. However, there was no evidence of carcinogenicity in small groups of rats given fluorouracil orally at doses of 0.01, 0.3, 1 or 3 mg per rat 5 days per week for 52 weeks, followed by a six-month observation period. Also, in other studies, 33 mg/kg of fluorouracil was administered intravenously to male rats once a week for 52 weeks followed by observation for the remainder of their lifetimes with no evidence of carcinogenicity. Female mice were given 1 mg of fluorouracil intravenously once a week for 16 weeks with no effect on the incidence of lung adenomas. On the basis of the available data, no evaluation can be made of the carcinogenic risk of fluorouracil to humans.
Mutagenesis
Oncogenic transformation of fibroblasts from mouse embryo has been induced in vitro by fluorouracil, but the relationship between oncogenicity and mutagenicity is not clear. Fluorouracil has been shown to be mutagenic to several strains of Salmonella typhimurium, including TA 1535, TA 1537 and TA 1538, and to Saccharomyces cerevisiae, although no evidence of mutagenicity was found with Salmonella typhimurium strains TA 92, TA 98 and TA 100. In addition, a positive effect was observed in the micronucleus test on bone marrow cells of the mouse, and fluorouracil at very high concentrations produced chromosomal breaks in hamster fibroblasts in vitro.
Impairment of Fertility
Fluorouracil has not been adequately studied in animals to permit an evaluation of its effects on fertility and general reproductive performance. However, doses of 125 or 250 mg/kg, administered intraperitoneally, have been shown to induce chromosomal aberrations and changes in chromosomal organization of spermatogonia in rats. Spermatogonial differentiation was also inhibited by fluorouracil, resulting in transient infertility. However, in studies with a strain of mouse which is sensitive to the induction of sperm head abnormalities after exposure to a range of chemical mutagens and carcinogens, fluorouracil did not produce any abnormalities at oral doses of up to 80 mg/kg/day. In female rats, fluorouracil, administered intraperitoneally at weekly doses of 25 or 50 mg/kg for 3 weeks during the pre-ovulatory phases of oogenesis, significantly reduced the incidence of fertile matings, delayed the development of pre- and post-implantation embryos, increased the incidence of pre-implantation lethality and induced chromosomal anomalies in these embryos. In a limited study in rabbits, a single 25 mg/kg dose of fluorouracil or 5 daily doses of 5 mg/kg had no effect on ovulation, appeared not to affect implantation and had only a limited effect in producing zygote destruction. Compounds such as fluorouracil, which interfere with DNA, RNA and protein synthesis, might be expected to have adverse effects on gametogenesis.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category D.
See WARNINGS section.
Nonteratogenic Effects
Fluorouracil has not been studied in animals for its effects on peri- and postnatal development. However, fluorouracil has been shown to cross the placenta and enter into fetal circulation in the rat. Administration of fluorouracil has resulted in increased resorptions and embryolethality in rats. In monkeys, maternal doses higher than 40 mg/kg resulted in abortion of all embryos exposed to fluorouracil. Compounds which inhibit DNA, RNA and protein synthesis might be expected to have adverse effects on peri- and postnatal development.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether fluorouracil is excreted in human milk. Because fluorouracil inhibits DNA, RNA and protein synthesis, mothers should not nurse while receiving this drug.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in children have not been established.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Stomatitis and esophagopharyngitis (which may lead to sloughing and ulceration), diarrhea, anorexia, nausea and emesis are commonly seen during therapy.
Leukopenia usually follows every course of adequate therapy with fluorouracil. The lowest white blood cell counts are commonly observed between the 9th and 14th days after the first course of treatment, although uncommonly the maximal depression may be delayed for as long as 20 days. By the 30th day the count has usually returned to the normal range.
Alopecia and dermatitis may be seen in a substantial number of cases. The dermatitis most often seen is a pruritic maculopapular rash usually appearing on the extremities and less frequently on the trunk. It is generally reversible and usually responsive to symptomatic treatment.
Other adverse reactions are:
Hematologic:
pancytopenia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, anemia.
Cardiovascular:
myocardial ischemia, angina.
Gastrointestinal:
gastrointestinal ulceration and bleeding.
Allergic Reactions:
anaphylaxis and generalized allergic reactions.
Neurologic:
acute cerebellar syndrome (which may persist following discontinuance of treatment), nystagmus, headache.
Dermatologic:
dry skin; fissuring; photosensitivity, as manifested by erythema or increased pigmentation of the skin; vein pigmentation; palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, as manifested by tingling of the hands and feet followed by pain, erythema and swelling.
Ophthalmic:
lacrimal duct stenosis, visual changes, lacrimation, photophobia.
Psychiatric:
disorientation, confusion, euphoria.
Miscellaneous:
thrombophlebitis, epistaxis, nail changes (including loss of nails).
OVERDOSAGE
The possibility of overdosage with fluorouracil is unlikely in view of the mode of administration. Nevertheless, the anticipated manifestations would be nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, gastrointestinal ulceration and bleeding, bone marrow depression (including thrombocytopenia, leukopenia and agranulocytosis). No specific antidotal therapy exists. Patients who have been exposed to an overdose of fluorouracil should be monitored hematologically for at least four weeks. Should abnormalities appear, appropriate therapy should be utilized.
The acute intravenous toxicity of fluorouracil is as follows:
| Species | LD50 (mg/kg ±S.E.) |
|---|---|
| Mouse | 340 ± 17 |
| Rat | 165 ± 26 |
| Rabbit | 27 ± 5.1 |
| Dog | 31.5 ± 3.8 |
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
General Instructions
Fluorouracil Injection, USP should be administered only intravenously, using care to avoid extravasation. No dilution is required.
All dosages are based on the patient's actual weight. However, the estimated lean body mass (dry weight) is used if the patient is obese or if there has been a spurious weight gain due to edema, ascites or other forms of abnormal fluid retention.
It is recommended that prior to treatment each patient be carefully evaluated in order to estimate as accurately as possible the optimum initial dosage of Fluorouracil Injection, USP.
Dosage
Twelve mg/kg are given intravenously once daily for four successive days. The daily dose should not exceed 800 mg. If no toxicity is observed, 6 mg/kg are given on the 6th, 8th, 10th and 12th days unless toxicity occurs. No therapy is given on the 5th, 7th, 9th or 11th days. Therapy is to be discontinued at the end of the 12th day, even if no toxicity has become apparent.
Poor risk patients or those who are not in an adequate nutritional state should receive 6 mg/kg/day for three days. If no toxicity is observed, 3 mg/kg may be given on the 5th, 7th and 9th days unless toxicity occurs. No therapy is given on the 4th, 6th or 8th days. The daily dose should not exceed 400 mg.
A sequence of injections on either schedule constitutes a "course of therapy."
Maintenance Therapy
In instances where toxicity has not been a problem, it is recommended that therapy be continued using either of the following schedules:
- Repeat dosage of first course every 30 days after the last day of the previous course of treatment.
- When toxic signs resulting from the initial course of therapy have subsided, administer a maintenance dosage of 10 to 15 mg/kg/week as a single dose. Do not exceed 1 g per week.
The patient's reaction to the previous course of therapy should be taken into account in determining the amount of the drug to be used, and the dosage should be adjusted accordingly. Some patients have received from 9 to 45 courses of treatment during periods which ranged from 12 to 60 months.
Handling and Disposal
Procedures for proper handling and disposal of anticancer drugs should be considered. Several guidelines on this subject have been published.1 to 7 There is no general agreement that all of the procedures recommended in the guidelines are necessary or appropiate.
Note: Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.If a precipitate occurs due to exposure to low temperatures, resolubilize by heating to 140°F and shaking vigorously; allow to cool to body temperature before using.
Directions for proper use of pharmacy bulk package
(Not for Direct Infusion)
The 50 mL and 100 mL Pharmacy Bulk Packages are for use in a Pharmacy Admixture Service only. They should be inserted into a plastic hanging device and suspended as a unit in a laminar flow hood. Use only if clear and seal is intact and undamaged.
Use of this product is restricted to a suitable work area, such as a laminar flow hood. Use only if clear and seal is intact and undamaged. Prior to entering the vial, remove the flip-off seal and cleanse the rubber closure with a suitable antiseptic agent. The container closure may be penetrated only one time, utilizing a suitable sterile transfer device or dispensing set which allows measured distribution of the contents. The date and time the vial was initially opened should be recorded in the space provided on the vial label. Transfer individual dose(s) to appropriate intravenous infusion solutions. Use of a syringe with a needle is not recommended. Multiple entries increase the potential of microbial and particulate contamination.
The withdrawal of container contents should be accomplished without delay using aseptic technique. However, should this not be possible, a maximum time of 4 hours from initial closure entry is permitted to complete fluid transfer operations. It is recommended that the transferred fluids be used promptly.
Instructions to Hang Vial
- Place oval portion of ring sling over vial neck
- Push bottom of vial through inner circle
- Hang vial using outer circle
Recommended Storage Conditions After Opening
Keep under laminar flow hood at room temperature.
HOW SUPPLIED
Fluorouracil Injection, USP is available in two pharmacy bulk vials as follows:
| Fluorouracil Injection, USP | Volume |
|---|---|
| 50 mg/mL | 2.5 g/50 mL vial |
| 50 mg/mL | 5 g/100 mL vial |
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.] Protect from light. Retain in carton until time of use.
Note: Although fluorouracil solution may discolor slightly during storage, the potency and safety are not adversely affected.
Also available as follows:
| Fluorouracil Injection, USP | Volume |
|---|---|
| 50 mg/mL | 500 mg/10 mL vial |
| 50 mg/mL | 1 g/20 mL vial |
10 mL vials are packaged 10 vials per shelf pack.
20 mL vials are packaged 10 vials per shelf pack.
REFERENCES
- Recommendations for the Safe Handling of Parenteral Antineoplastic Drugs. NIH Publication No. 83-2621. For sale by Superintendent of Documents, US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC 20402.
- AMA Council Report. Guidelines for Handling Parenteral Antineoplastics. JAMA, 1985; 253 (11):1590–1592.
- National Study Commission on Cytotoxic Exposure- Recommendations for Handling Cytotoxic Agents. Available from Louis P. Jeffrey, ScD, Chairman, National Study Commision on Cytotoxic Exposure, Massachusetts College of Pharmacy and Allied Health Sciences, 179 Longwood Avenue, Boston, Massachusetts 02115.
- Clinical Oncological Society of Australia: Guidelines and Recommendations for Safe Handling of Antineoplastic Agents. Med J Ausralia. 1983, 1:426–428.
- Jones RB, et al: Safe Handling of Chemotherapeutic Agents: A Report from the Mount Sinai Medical Center. CA-A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 1983; (Sept/Oct) 258–263.
- American Society of Hospital Pharmacists Technical Assistance Bulletin on Handling Cytotoxic and Hazardous Drugs. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1990; 47: 1033–1049.
- OSHA Work-Practice Guidelines for Personnel Dealing with Cytotoxic (Antineoplastic) Drugs. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1986; 43:1193–1204.
Product Glimpse
Description
We are committed to work towards a healthier and happier world. The company is an integrated, research based international pharmaceutical company, producing a wide range of quality, affordable generic (Fluorouracil 250mg/5ml Injection) medicines, trusted by health-care professionals and patients across geographies.
We offer you the highest quality new Generic medicines ie. Fluorouracil 250mg/5ml Injection, drugs and also with innovative packing at the lowest prices shipped to you from India. Browse our latest Pharmaceuticals and Generics possibilities and other pharmaceuticals possibilities…more.